|
|
|
Probiotics
14.12.05 18:23
|
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Probiotics
- Culture media and protective agent to culture microorganism in the following table or such mixtures or embryoid - Functional effect: Can help proliferation of lactic acid bacteria, the inhibition of harmful bacteria, and fecal improvement - Daily Intake : 100,000,000 ~ 10,000,000,000 CFU (Source: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety)
What is Probiotics? It refers to living bacteria with good effect on health of a human body. Most types of probiotics known up to date are lactic acid bacteria. Since a Russian scientist Elie Mechinikoff revealed the secret of Bulgarian longevity is Lactobacillus-fermented milk and won the Novel prize, there have been many studies on functional effects of lactic acid bacteria and probiotics. To be probiotics, bacteria and lactic acid bacteria must survive in gastric acid and bile acid and reach small intestine to proliferate and settled in intestines, showing good effects. Plus, they should be non-pathogenic without poisoning.
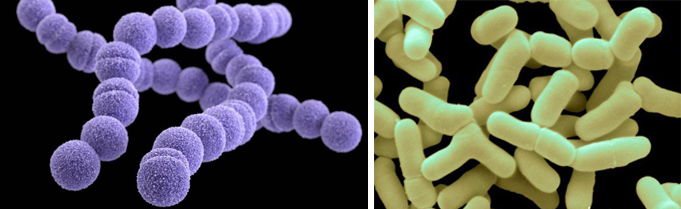
l Probiotics: Streptococcus and Bifidobacterium
Effect of Probiotics
1. Proliferations beneficial bacteria and inhibits harmful bacteria, to create healthy intestinal environment.
Once probiotics is taken and living beneficial bacteria settled in intestines, it creates lactic acid and makes acidified intestinal environment. The harmless bacteria will reduce in the number, because it does not survive acidified environment. Well-grown and developed in oxidation, beneficial bacteria further proliferation to help desirable intestinal bacterial flora well settled.
This beneficial bacteria is first settled between intestinal cellular processes with irregular surface, in order to remove place where harmless bacteria can stick with. In addition, this creates antimicrobial substance such as bacteriocin that inhibits the growth of harmless bacteria.
2. Strengthens intestinal functions.
Beneficial resident bacteria are essential to maintain strong intestinal membrane. Beneficial bacteria helps form ‘tight coupling’ to prevent malignant substance from passing through intestinal epithelial cells. Once reduced in the number of beneficial bacteria, the space between epithelial cells gets loose, there can be increase in the inflow of malignant substance.
3. Forms healthier immune system
About 80% of immune cells live in intestines. Most of
them live in lymphatic tissues inside the intestinal wall, adapting itself to
intestinal environment and learning the function each cell is to perform. In
this course, intestinal beneficial bacteria help immune cells cause
hypersensitive immune reaction. When beneficial bacteria reduced in the number,
immune cells grow difficult. And this may cause hypersensitive immune diseases
subject to skin diseases (food allergy, atopy).
Probiotics inhibits the activation of nuclear factor, thereby inhibiting inflammation reaction of intestinal immune system. It plays a role of stopping inflammation through induced secretion of cytokine, increasing the activity of natural killer cells.
5. Helps metabolism
Intestinal bacteria helps digestion through the secretion of enzyme so that food in stomach can be easily absorbed if not degraded. In addition, it generates monoenoic fatty acid by fermenting undegradable fiber and polysaccharide. It is involved in a variety of metabolism including the degradation and absorption of drug, intestinal water absorption, and the formation of vitamin. In addition, it improves lactose intolerance by degrading lactose.
6. Role of reducing cholesterol
Bile acid is composed of cholesterol, and most of bile
acid is absorbed for reuse, not being discharged after secretion. Probiotics
has effect of reducing re-absorption of bile acid. Bile acid is discharged if
not re-absorbed. When bile acid lacks, as liver reuses cholesterol to form
bile, it can finally contribute to reducing the concentration of cholesterol in
blood.
If intestinal harmful bacteria prevails, poisonous
substances (including ammonia, indole, skatole) is produced to contaminate
blood and put stress on liver. Lactic acid bacteria inhibit the reproduction of
harmful bacteria, thereby reducing endotoxin to relieve stress on liver.
If the intake of probiotics decreases the number of
harmful bacteria, the balance of intestinal bacterial flora is recovered, with
the effect of promoting the intestinal passage of food.
Food poisoning bacteria called Salmonella destructs
intestinal epithelial cells to invade into the human body. Probiotics inhibits
the intrusion of Salmonella by strengthening intestinal epithelial cells and
increasing tight coupling.
Lactic acid bacteria is settled not only in intestines and vagina but also in urethral mucous membrane, to prevent the intrusion of harmful bacteria.
11. Inhibits the growth of Helicobacter pylori, eliminating candidiasis
Probiotics-related Articles
1. (Intestinal health) Functional modulation of enterocytes by gram-positive and gram negative microorganisms. (Otte JM, Podolsky DK, Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286(4): G613-26(2004)
2. (Immunity) Probiotic induced suppression of allergic sensitization and airway inflammation is associated with an increase of T regulatory dependent mechanisms in a murine model of asthma (Feleszkop W, et al., Clinical & Experimental Allergy37(4): 498-505 (2007)
3. (Immunity, Infection) Hojsak, et al. Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of nosocomial gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections. Pediatrics 2010;125:e1171
4. (Immunity) Effect of a probiotic infant formula on infections in child care centers: comparison of two probiotic agents (Weizman Z, Asli G, et al., BMJ pediatrics 115(1):5-9(2005)
5. (Formation of vaccine) Probiotic bacteria stimulate vius specific neutralizing antibodies following a booster polio vaccination (Vrese m, Rautenberg P, et al., European journal of nutrition 44():406-413(2005)
6.(Atopy) Impact of maternal atopy and probiotic supplementation during pregnancy on infant sensitization: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. (Huurre A, Laitinen K, Rautava S, et al., Clin Exp Allergy. 2008 May 7.)
7. (Atopy) Kalliomaki, et al. Probiotics in primary prevention of atopic disease: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2001;357(9262):1076-1079
8. (Asthma, Rhinitis)Treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis with lactic acid bacteria. (Wang MF, et al., Pediatric allergy and immunology: official publication of the European Society of Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 15(2): 152-8 (2004)
9. (Traveler’s diarrhea) Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG as a Diarrheal Preventive in Travelers. (Hilton, et al., J. Travel Med. 1997:41-43)
10. (Chronic constipation) Lactobacillus casei rhamnosus Lcr35 in children with chronic constipation. (Bu LN, Chang MH, Ni YH, et al. Pediatr Int. 2007;49:485-90.)
11. (Inflammatory Bowel Diseases) Probiotics for maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis. (Naidoo K, Gordon M, Fagbemi AO, Thomas AG, Akobeng AK. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;12:CD007443)
12. (Jane Crohn's disease, Ulcerative colitis) Mechanisms of disease: pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (Sartor RB, Nature clinical practice Gastoroenterology & hepatology 3(7): 390-407 , 2006)
13. (Irritable bowel syndrome) The efficacy of probiotics in the therapy of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review (Moayyedi P, Ford AC, et al., Gut 2008)
14. (Cholesterol) One-year application of probiotic strain Enterococcus faecium M-74 decreases serum cholesterol levels. (Hlivak P, Odraska J, Ferencik M, et al., Bratisl Lek Listy. 2005;106:67-72.)
15. (Chronic liver disorder) Probiotics for patients with hepatic encephalopathy. (McGee RG, et al., Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Nov 9;11:CD008716)
16. (Vaginitis) Efficacy of vaginal probiotic capsules for recurrent bacterial vaginosis: a
double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. (Ya W, Reifer C, Miller LE. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;203(2):120.e1-6.)
17. (urinary tract infection) A long-term, multicenter, double-blind study of an escherichia coli extract (OM-89) in female patients with recurrent urinary tract infections. (Bauer HW, Alloussi S, Egger G, et al. Eur Urol. 2005;47:542-548.)
18. (Helicobacter pylori) Kefir improves the efficacy and tolerability of triple therapy in eradicating Helicobacter pylori. (Bekar O, Yilmaz Y, Gulten M. J Med Food. 2011;14(4):344-347.)
19. (Candidiasis) Improved treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis with fluconazole plus probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 and Lactobacillus reuteri RC-14. (Martinez RC, et al. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2009;48:269-74)
Probiotics of Chr.Hansen, Denmark
A Danish company Chr.Hansen specializes in making lactic acid bacteria products for 140 years. The company tops the global market share in the Nutrition & Health sector. Chr.Hansen is widely known and about 0.5 billion consumers a day use its lactic acid bacteria products.
The company produces lactic acid bacteria products whose effect is proved through over 450 academic papers and 80 verified clinical experiments. Based on long-time studies, stable species are strictly selected, while all the processes are under the system optimized into lactic acid bacteria processing.
Probiotics is known as varying on species. Chr.Hansen’s representative strains are effective and safe through sufficiently verified clinical study data.
LA-5? (Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5)
- Separated from the Chr.Hansen-affiliated starter culture bank
- It has been widely used worldwide as ingredients and supplements since 1979. No adverse effect has been reported.
- No adverse effect found in the results of clinical study, from new born babies to those in old age (Intake of lactic acid bacteria over 5*1010CFU daily)
- GRAS-certified by FDA(Food and Drug Administration)
- Approved as natural healthcare product by a Danish medical organization
- Function: intestinal function improvement, increased intestinal beneficial bacteria recovery after antibiotic treatment,
constipation improvement, improved stool status, bacterial flora and diarrhea
LGG-5? (Lactobacillus rhamnosus LGG)
- Found in the intestines of a healthy person
- It has been widely used worldwide as ingredients and supplements for 20 years. No adverse effect has been reported.
- No adverse effect found in the results of clinical study, from new born babies to those in old age (Intake of lactic acid bacteria over 5*1011CFU daily)
- Function: Diarrhea status improved by antibiotics, improved stool concentration during the antibiotics treatment
Enhanced immunity reaction after inoculation, reduced respiratory infection, relieved atopy,
Reduced risk of rotavirus virus infection, bacterial diarrhea |